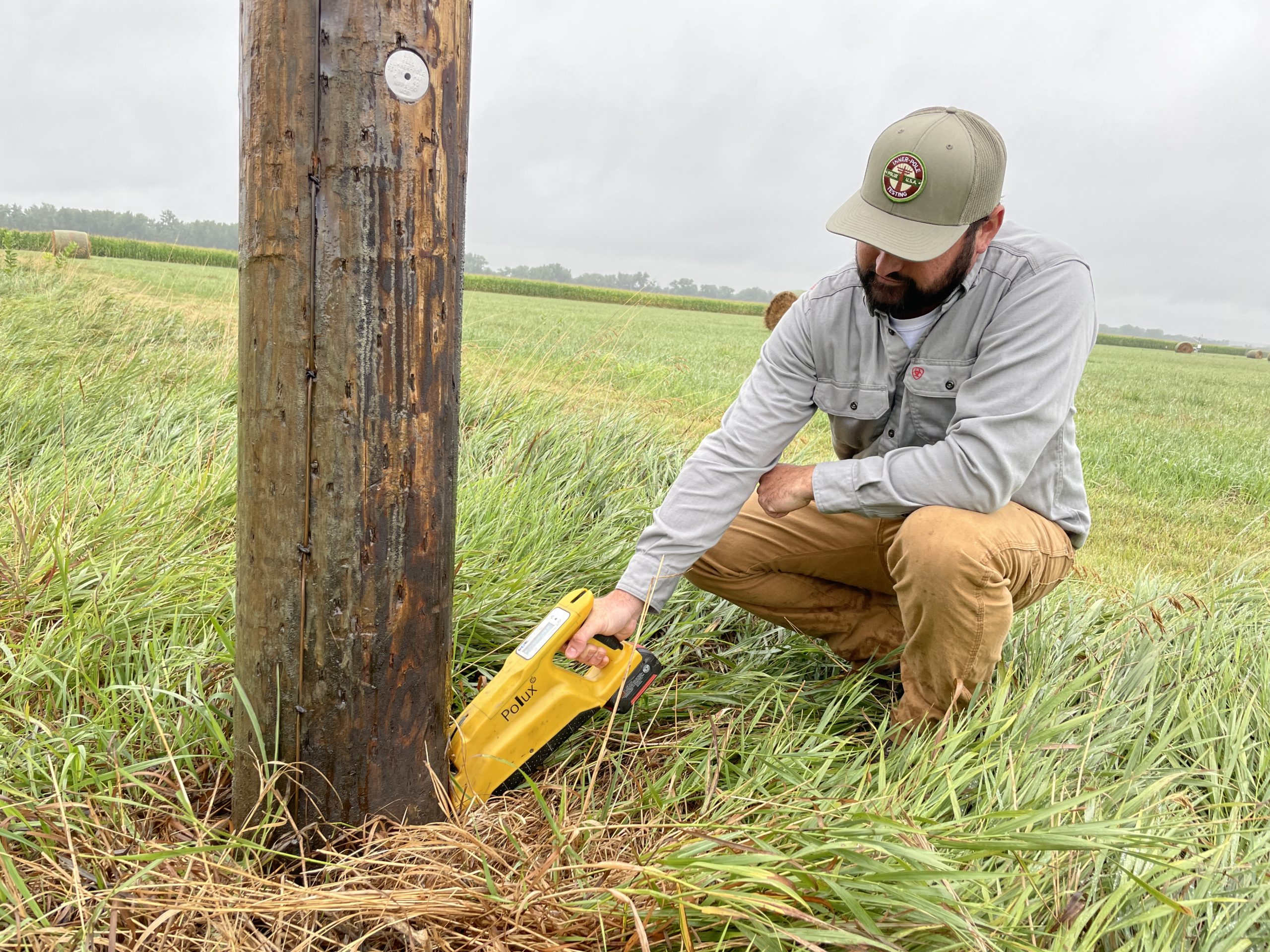
As a not-for-profit utility, Dawson PPD focuses on cost-effectively extending the life of its existing facilities while maintaining adequate levels of safety and reliability. Testing wooden poles helps the District ensure reliability and long life of its equipment, saving customers money in the long run.
Traditionally, pole testing involved a hammer for sounding, a shovel for digging around the base and drilling holes to test for decay. Today, Dawson PPD hires a contractor that uses a scientifically-based system called POLUX as a less-invasive and more accurate form of testing.
POLUX works by sending two, three inch long probes the size of an eight-penny nail into the base of the utility pole. This is the most vulnerable point where decay is most likely to occur on a pole. The probes measure resistance and moisture content of the pole. This information, along with the type of wood the pole is made of and how it was treated are run through a computer program with the pole’s GPS location recorded.
Typically, Dawson PPD uses a Southern Yellow Pine tree for its poles, which should have a resistance of 8,000 pounds per square inch when new. If the measurement falls below 50 percent of the recommended resistance, in this case 4,000 PSI, the pole is marked for replacement.
All of Dawson PPD’s poles are tested every 10 years on a rotating schedule with 10,000-11,000 poles tested annually.
OTHER NEWS
Between the lines: Technology, the grid and Dawson PPD. (Part 1)
Dawson PPD’s electric distribution utility system is a complex network of wires, transformers and other equipment that delivers electricity from power plants to substations to homes and businesses. In recent years, there have been several new technologies that have been developed to improve the efficiency, reliability and security of the electric distribution system.
Dawson PPD’s swift response to tornado demonstrates commitment to service
Dawson PPD quickly made repairs after May 5, 2023, tornado at Johnson Lake, Nebraska
Working together for irrigators
The Twin Platte Natural Resource District needed to document irrigation groundwater usage. They could have installed water meters, but the meters were not cost effective. And water meters traditionally are only read once a year, after irrigation season. Instead, they...